Immune/Lymphatic System:
The immune system is our body’s defense system against infections and diseases. Cells, tissues and organs work together to respond to dangerous organisms like viruses, fungi or bacteria that may enter the body from the environment. There are three types of response systems in the immune system: the anatomic response, the inflammatory response, and the immune response.
• The anatomic response prevents threatening substances from entering your body. An example of the anatomic system would be the skin. If substances do get by, the inflammatory response goes on attack.
• The inflammatory system works by excreting the invaders from your body through fever, sneezing, and runny noses.
• When the inflammatory response fails, the immune response goes to work. This is the central part of the immune system that is made up of white blood cells, which fight infection. About a quarter of white blood cells, called the lymphocytes, migrate to the lymph nodes and produce antibodies, which fight disease.
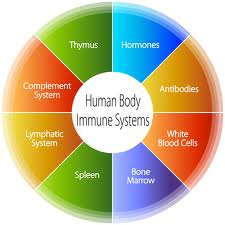
The organs of the immune system are called the lymphoid organs that affect a type of white blood cells. The organs of the lymphoid system are:
• Adenoids are masses of lymphoid tissue in the upper part of throat behind the nose that trap bacteria and viruses as you inhale.
• Appendix function is unknown.
• Blood vessels carry blood.
• Bone marrow is the located in the center of bones and is where red blood cells are manufactured.
• Lymph nodes are located throughout the body and acts as filters, removing bacteria, fluids and cancer cells that travel through the lymphatic system.
• Lymphatic vessels carry lymph.
• Peyer’s Patches are lymph follicles on the mucosa of the small intestines and play a role in immunological response.
• The spleen is an organ that contains white blood cells
• Thymus is important for the development of the immune system in children, as the T cells develop in the thymus. The thymus shrinks with age.
• Tonsils help to trap bacteria and viruses as you breathe.
The lymphatic system is a subdivision of the immune system that filters out organisms that cause disease, produces white blood cells, and generates disease-fighting antibodies. It also distributes fluids and nutrients in the body and drains excess fluids and protein so that tissues do not swell. It does not contain blood, but rather lymph, which is formed from the fluid surrounding body cells and diffused into lymph vessels.
Problems of the immune system:
Diseases and problems with the immune system can be divided into two basic categories. Those in which the body’s ability to fight disease is impaired and those in which the immune system overreacts to stimuli, causing damage to the other organs or systems of the body.
AIDS or acquired deficiency syndrome is an infectious disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV, which destroys immune cells and can affect the body’s organ systems.
Autoimmune diseases are diseases in which the immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissues. There are more than eighty types of autoimmune disorders, including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, Hashimoto thyroiditis and Sjogren’s syndrome.
Allergies are an abnormality high sensitivity to substances such as foods, pollens, molds, and/or microorganisms. There is a correlation between asthma and allergies.
To maintain a healthy immune system don’t smoke, eat a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in saturated fat, exercise regularly, maintain a healthy weight, control your blood pressure, if you drink alcohol, drink only in moderation, get adequate sleep, take steps to avoid infection, such as washing your hands frequently and cooking meats thoroughly, get regular medical screening tests for people in your age group and risk category.